Table of Contents
What is Aging?
Aging is defined as a genetic physiological process associated with morphological and functional changes in cellular and extracellular components aggravated by injury throughout life and resulting in a progressive imbalance of the control regulatory systems of the organism, including hormonal, autocrine, neuroendocrine and immune homeostatic mechanisms.
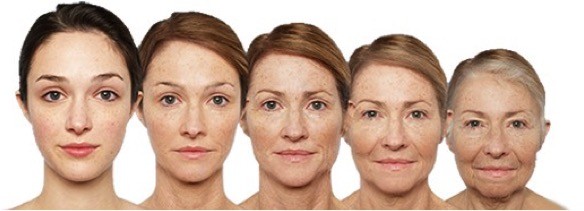
Factors That Control Aging
Aging is a natural process and an inevitable fact of life. Every one eventually ages despite the best of efforts and care; however, how you succumb to age is subjective and tends to vary between individuals.
Several factors influence the way you age. Depending on these factors you may age gracefully and be a sight for sore eyes or you may ‘fall from grace’ and be a sore sight for all eyes. Factors that influence aging can be categorized as intrinsic (internal) and extrinsic (external) factors.

Top 8 Extrinsic Factors For Aging
Several external triggers influence the way you age. They may be environmental factors or your own lifestyle choices. Let us take a peek-a-boo at a few of them.
1. Sunlight
The sun sustains life on earth but overexposure to the sun rays speeds up the aging process. The free radicals produced by the UV rays damage the DNA in skin cells, impair collagen production, destroy elastin and ruin your skin’s ability to regenerate and repair.
With time, unappealing changes such as dark spots, dryness, and freckles, appear on the skin. The collective harm done by the sun is known as photodamage.
Your ability to endure the sun entirely depends on your skin type and the degree of exposure to sunlight. Dark skins, with more melanin, are more sun tolerant than fair skins; as a result, they tend to age slower.
2. Excessive Alcohol
It is all very well to enjoy a ‘shot on the rocks’ but remember that alcohol is an established neurotoxin, which speeds up the normal aging process.
Excessive alcohol makes a person more vulnerable to various diseases of the heart and liver, and dehydrates the skin, contributing to a dull and aged look.
3. Stress
Are you the kind of person who worries in a hurry? Beware! A person’s ability to handle stress has a great influence on the way he ages.
Oodles of energy is required to deal with stress-causing factors and the rate at which this energy is expended controls the quality of aging.
4. Facial Exercises
A few facial exercises which were initially promoted as an antidote to aging are now believed to enhance wrinkles and emphasize facial lines
5. Unhealthy Diet
Look before you eat. If you are on a weight watch just remember that a poor, ill-balanced diet, will rob your skin of its natural sheen.
A greasy, jumbo diet can also affect your overall health and usher in premature aging!
6. Pollution
If you want to stay youthful for a long, long time stay away from the heat and dust! Pollution produces oxidants on the skin surface, which work on the skin cells and destroys them, thereby fast-forwarding the aging process.
7. Cigarette Smoking
Nicotine breaks down skin cells at a faster pace. As a result, long-time smokers develop wrinkles and a sallow, sagging skin.
But the good news is that if the smoker ‘kicks the butt’ the detrimental effects of smoking can be successfully reversed and visibly improved skin will be there for all to see.
Therefore, it is never too late to stop your life from going up in smoke!
8. Foods to Help Fight the Effects of Aging
Most of us are keen to stay looking as fresh and young as possible, and although there’s no way to pause or turn back the clock, there are few age proof strategies we can employ to make sure we stay looking good.
Maintaining a healthy and well-balanced diet is one approach, and the good thing is that some foods are thought to give us extra ammunition when it comes to combating the signs of aging.
“Superfood” is an informal term for foods that benefit the body in many different ways. Superfoods help to meet several dietary needs and are great sources of essential vitamins and minerals also fight disease and sickness, making them powerful anti-aging tools. Some top anti-aging foods are listed below;

11 Incredible Anti-Aging Super Foods
1. Berries
According to the American Chemical Society, Berries are one of the best sources of antioxidants. Plus, they’re rich in fiber and vitamin C to help keep your immune system, joints, and skin healthy.
They may even help stave off memory loss and cognitive decline. They’re also low in calories with a high water content.
All berries have benefits, but blueberries, cranberries, blackberries, raspberries, and strawberries have the most antioxidants.
Try to choose fresh berries when they’re in season, but unsweetened frozen berries are a good option in the off-season.
You can eat berries in a variety of ways: add them as a topping to cereals and salads, toss them into a smoothie before blending or eat them as a sweet snack.
- Blackberry Tea: Health Benefits, Uses, Recipes, Side Effects And More
- 12 Best Tips Of Growing Strawberries: How To Care For Strawberries?
2. Fish
Fish contains heart-healthy and inflammation-fighting omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Eating fish at least once a week may help prevent age-related memory loss. Choose cold-water, fatty fish like salmon, lake trout, herring, sardines, and tuna.
Try to eat at least two servings of omega-3-rich fish per week. One serving is about 3.5 ounces, or about the size of a deck of cards.
Try to replace other meats in your diet with fatty fish, or add canned tuna or salmon to salads instead of chicken or cheese. Stick with fish that has been baked or broiled, not deep-fried.
3. Olive Oil
Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats, which may help lower cholesterol and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Choose your oil carefully: Look for a fresh variety of extra virgin olive oil. Do not purchase oil that is more than one year old because the health benefits may diminish over time.
Be sure to store it in a cool, dark place. Since it is high in calories, it’s important to use it in moderation. Use olive oil in place of other fatty foods (like butter or stick margarine), not in addition to them.
Use it also to make your salad dressings or lightly coat vegetables to enjoy as a side dish.
- 9 Proven Benefits of Olive Leaf Extract: Uses, Warnings & More
- 15 Unbelievable Benefits Of Olive & Olive Oil And Olive Seed
- 11 Amazing Medicinal Health Benefits Of Olive Leaf (Olea Europaea)
4. Dark Leafy Greens
Dark, leafy green vegetables are loaded with vitamins, minerals, and disease-fighting phytochemicals to help protect your skin, vision, heart, and brain. The carotenoids in dark, leafy greens may help stop the growth of certain types of cancer cells.
Plus, they’re rich in fiber to help keep you feeling full longer and water to keep you hydrated. Kale, collards, turnip greens, swiss chard, spinach, mustard greens, and broccoli are all excellent choices. It’s best to purchase dark, leafy greens fresh, when possible.
Look for the ones that have darker green leaves with no yellowing or wilting, and always wash them before eating.
There are endless options for adding greens to your diet. Toss them in soups or smoothies, make “green” kale chips, or sauté them with spices and seasonings.
To help your body absorb all of the nutrients, add one to two teaspoons of olive oil.
Note: People who take certain blood thinners may need to avoid eating leafy greens. Talk to your doctor to find out if you fall into this category.
- Bay Leaf Tea: Health Benefits, Uses, Side Effects, Warnings And More
- Sycamore Leaf: Health Benefits, Uses, Recipes And More (Plane Leaves)
- Bay Leaf: Health Benefits, Uses, Side Effects and Warning (Laurel Leaf)
- Mulberry Leaf and Mulberry Tea: Health Benefits, Uses, Side Effects, and Warning
5. Nuts And Seeds
Nuts and seeds are a good source of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, plant-based protein, filling fiber, vitamins, nutrients, and antioxidants.
They may even help reduce the risk of heart disease because the naturally-occurring plant sterols and L-arginine can help lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in the blood and protect the lining of the arteries.
Most varieties of nuts are healthy, but walnuts, almonds, pistachios, hazelnuts, and pecans are particularly beneficial.
But watch out for salted nuts or chocolate-covered nuts; instead, stick with raw, unsalted nuts. For seeds, look for ground flaxseed, soaked chia seeds, and hemp seeds.
To incorporate them into your diet, add an ounce of chopped nuts or a tablespoon of seeds to your cereal, yogurts, salad or smoothie.
You can also eat them as a snack, or have a nut-butter sandwich on whole-grain bread. Remember: They can be high in calories, so practice moderation.
- Hazelnuts: Health Benefits & Nutrition Facts, Can You Eat Hazelnuts?
- Top 17 Best Health Benefits Of Peanuts (Mungfali) & Pine Nuts
6. Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate is rich in powerful antioxidants (flavonoids and polyphenols) linked to reduced inflammation, lower blood pressure, and better brain health.
These benefits come from dark chocolate only; not milk or white chocolate. The darker the chocolate, the better; look for a bar that is at least 70 percent cocoa.
Practice moderation: you only need one to three ounces per day to get benefits. Avoid chocolate that contains added fat, sugar, and calories. Don’t replace healthy foods with dark chocolate; instead, switch it out with other treats.
7. Yogurt
Yogurt is rich in calcium and protein. It may help restore balance in the digestive system via probiotics, prevent high blood pressure16, and keep bones strong and healthy.
Choose varieties that are low in sugar, and contain active cultures, probiotics, and vitamin D. For more protein, you may want to try Greek yogurt.
Yogurt can be eaten for breakfast or as a snack. You may want to add some mix-ins like flaxseed, nuts, granola or berries.
You can also blend it into smoothies, or use it as a replacement for sour cream, oil or butter in recipes.

8. Legumes
Legumes include beans, peas, and lentils, are packed with complex carbohydrates, fiber, protein, and antioxidants.
Their high-fiber content may help keep your digestive system healthy, scrub away LDL cholesterol to protect your heart, and keep blood sugar levels steady.
Reach for a variety of beans (black, kidney, garbanzo, pinto, cannellini, lima, navy, great northern), peas (black-eyed, whole or split) and lentils (green, red, yellow and black).
Peanuts are another great option in the legume family. There are many ways to add beans, peas, and lentils to your meals. Choose them as a side dish, or add them to salads, soups and pasta dishes.
9. Whole Grains
Whole grains are an excellent source of fiber, vitamins (especially B vitamins), and antioxidants. Research from the Journal of Nutrition shows that whole grains may help reduce the risk of heart disease, improve insulin sensitivity, aid in digestion and help with weight maintenance.
All whole grains are healthy, but oatmeal, quinoa, barley, cracked-wheat, and brown rice are good examples. Shop smart! Look for 100 percent whole wheat or whole grain.
Despite their benefits, the average American eats less than one serving of whole grains each day. The USDA recommends at least three to five servings daily.
All it takes is some simple swaps: Use whole wheat bread and tortillas instead of the white, refined versions; use wild or brown rice or whole-wheat pasta as a side dish, and start your day off right with oatmeal or whole-grain cereal for breakfast.
10. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes contain vitamins A, C, and B6, as well as minerals like potassium, magnesium, manganese, calcium, and iron. They’re also a great source of vitamin A, which promotes good vision and has anti-aging benefits.
Potassium and magnesium help regulate blood pressure. Sweet potatoes come in a variety of colors. The orange and yellow types contain the most vitamin A; the purple and red types are an excellent source of antioxidants.
Try to eat sweet potatoes with the skin to get the maximum amount of fiber and nutrients. Trade your traditional white baked potato for a sweet potato. You can also add roasted sweet potatoes to salads.
4 Steps With Picture: How To Grow Potatoes In The Bag & At Home
11. Garlic
Garlic has anti–oxidant, antiseptic, antibacterial, and antiviral properties.
While it is used to help treat intestinal, respiratory and skin infections, its most important use is to help reduce high blood pressure, lower levels of harmful blood fats, (LDL cholesterol, triglycerides), reduce blood stickiness, dilate blood vessels and improve peripheral blood flow.
Summary
Aging not only alters our physical appearance due to changes in skin, bones, and muscle tone but also affects our internal organs.
The heart and immune system become less efficient, and diseases that are rare in young people become increasingly more prevalent in older adults.
Lots of people are looking for the fountain of youth. Believe it or not, the foods you eat may have a big impact on how you age.








